Patented Technology
Advantages of Bio-Fermentation vs. Chemical Synthesis for Long-chain Dicarboxylic Acids Production
1. Introduction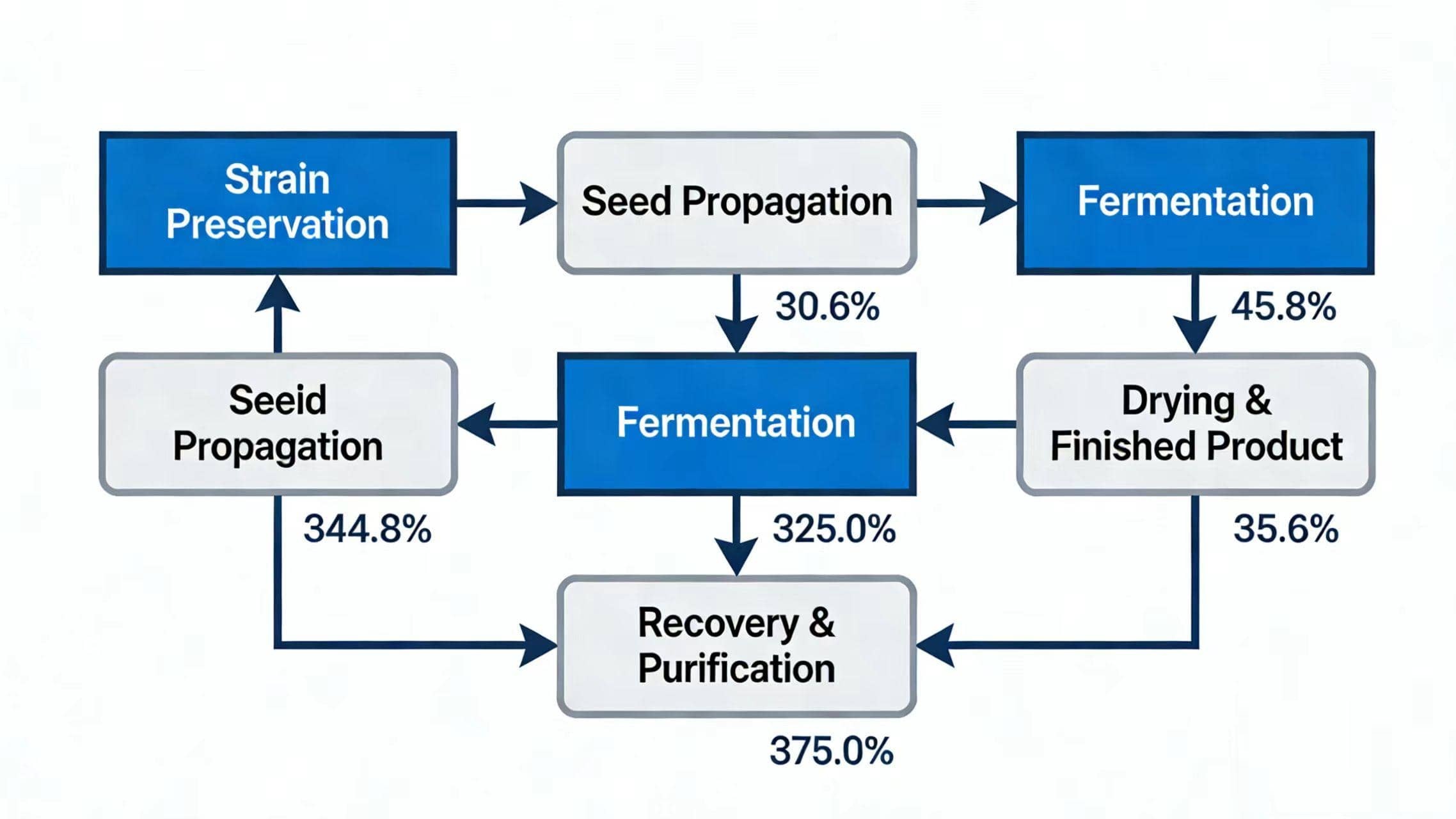
Long-chain dicarboxylic acids(typically C8-C18) are high-value chemical intermediates widely used in premium polymers, corrosion-resistant coatings,
high-performance lubricants, fragrances, and pharmaceuticals. Historically, their production relied on chemical synthesis, which involves multiple complex steps under extreme conditions. Our company has pioneered and commercialized a proprietary bio-fermentation process that offers significant technical, economic, and environmental benefits.
2. Key Advantages of Patented Bio-Fermentation Technology
2.1. Superior Selectivity and Product Purity
· Chemical Synthesis: Typically requires harsh catalysts (e.g., strong acids, heavy metals) and operates under high temperature and pressure. It often leads
to undesirable side reactions, generating isomers and by-products. Subsequent purification is complex, energy-intensive, and can reduce final yield.
· Bio-Fermentation: Utilizes specifically engineered microbial strains as "cell factories." These microorganisms naturally or selectively oxidize alkanes or fatty
acids into target LCDAs with high enzymatic specificity. This results in exceptional product purity (>99%), minimal by-products, and a consistent, single-isomer
profile crucial for demanding applications like medical-grade polymers.
2.2. Milder Process Conditions & Enhanced Safe· Chemical Synthesis: Operates at high temperatures (often 200-400°C) and pressures, requiring specialized,
costly alloy equipment. Processes involve hazardous reagents, posing significant operational safety risks and high insurance costs.
· Bio-Fermentation: Conducted in aqueous medium at near-ambient temperature (30-40°C) and atmospheric pressure.This dramatically lowers energy
consumption and allows the use of standard fermentation and downstream equipment, reducing capital expenditure and improving workplace safety.
2.3. Environmental Sustainability & Green Chemistry Alignmen
· Chemical Synthesis: Generates substantial chemical waste, including spent catalysts (often containing heavy metals), organic solvents, and acidic/alkaline
wastewater. Treatment of this waste is costly and has a higher environmental footprint.
· Bio-Fermentation: Employs renewable feedstocks (e.g., plant-derived oils or alkanes). The process is aqueous-based, significantly reducing the use of toxic
organic solvents. Microbial catalysts are biodegradable. Overall, it offers a dramatically reduced carbon footprint, lower wastewater toxicity,and aligns perfectly
with green chemistry and circular economy principles, which is increasingly valued by global partners and regulators.
2.4. Flexibility and Scalability for Diverse Product Portfolio
· Chemical Synthesis: Producing different chain-length LCDAs (e.g., DC12 vs. DC14) often requires separate, tailored synthsis routes or extensive post-synthesis
separation, limiting flexibility.
· Bio-Fermentation: Through advanced metabolic pathway engineering, we can tailor our proprietary microbial strains to efficiently produce specific chain-length
dicarboxylic acids (from DC10 to DC18) by simply modifying the fermentation substrate or process parameters. This provides unmatched flexibility to meet diverse
market needs from a single,scalable platform technology.
2.5. Economic Viability in the Long Term
While the R&D and strain development for bio-fermentation are intensive, the operational economics
are favorable:
· Lower energy and utility costs.
· Reduced spending on hazardous material handling and waste treatment
· Higher-value products due to superior purity and sustainability credentials command premium pricing.
· As the technology scales and renewable feedstock costs decrease, the cost advantage continues to grow.
3. Conclusion
Our patented bio-fermentation technology represents a paradigm shift in long-chain dicarboxylic acid
manufacturing. It replaces the energy-intensive, hazardous,and waste-generating chemical synthesis with
a precise, safe, sustainable, and efficient biological process. This technology not only ensures we supply
products of the highest and most consistent quality to our global customers but also firmly positions us and
our partners at the forefront of sustainable industrial biotechnology.
We are committed to leveraging this cutting-edge technology to reliably serve the global market with premium, eco-friendly biochemical solutions.

